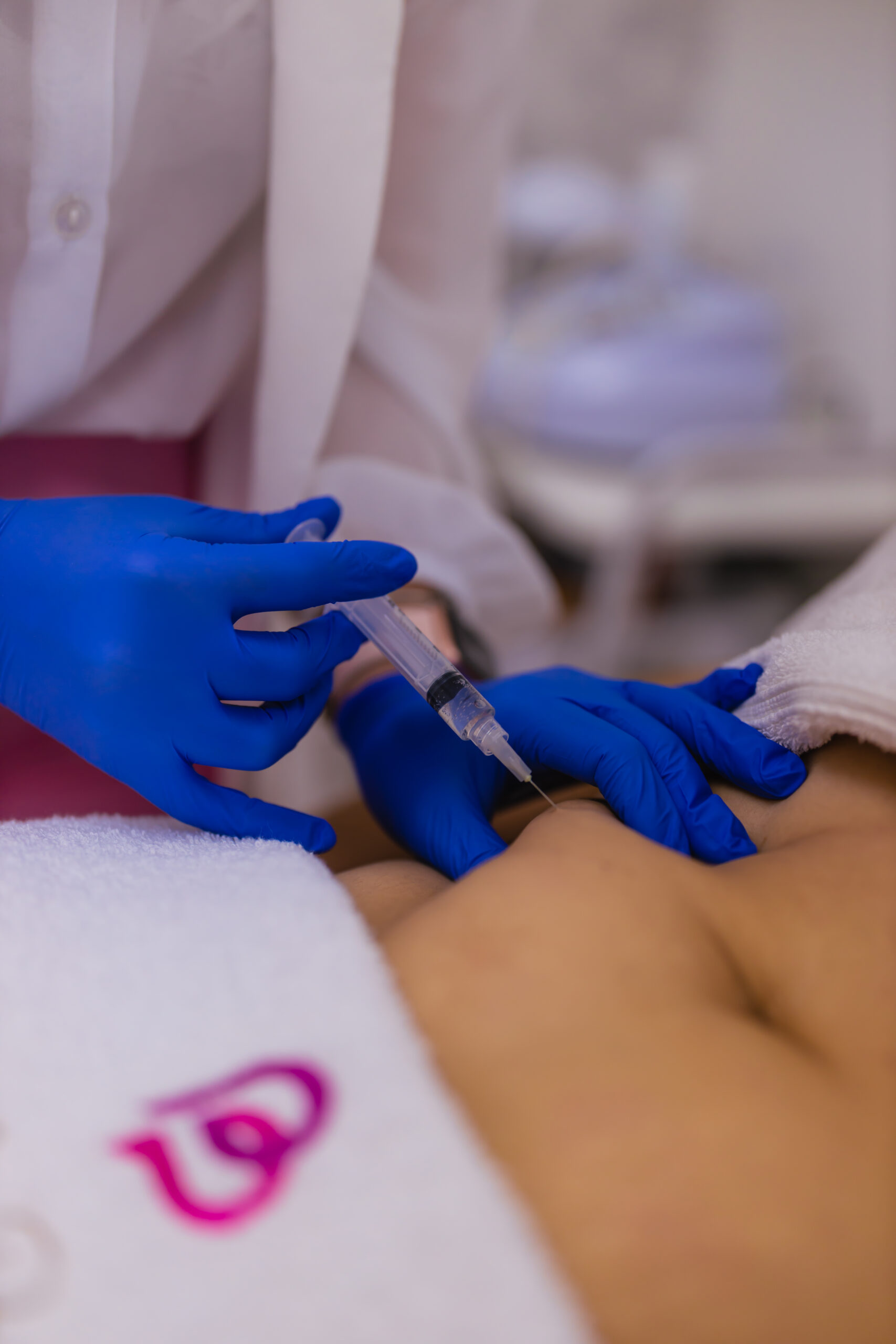
Injection lipolysis and sagging is an injection of a special drug for weight loss. They are injected subcutaneously into problem areas on the body. This enzyme therapy are used as fat-destroying drugs.
What are lipolytics?
Lipolytics are drugs that activate the destruction of fat cells. All lipolytics are composed of natural substances. Depending on the principle of action, two types of lipolytics are distinguished:
- direct – destroy cells with fat, and the products of this decay are naturally excreted from the body. Direct lipolytics include sodium deoxycholate, phosphatidylcholine;
- indirect – they act indirectly, fat is burned by activation of biochemical processes, but the fat cell itself is not destroyed. These lipolytics are more often used in places with a relatively thin body fat (for example, the face area).
One injection affects body fat over an area of 20 cm2. Depending on the area and depth of the problem area, 1 to 4 procedures are recommended with an interval of 15 days.
Lipolitics are issued and introduced as a combination of the finished drug and pain medication, so the procedure is quite comfortable for the patient.
What are enzymes?
Enzymes (enzymes) are protein compounds that are contained in the body and act as catalysts for metabolic processes. In their absence, biochemical processes in the body will be incomplete.
Injections of certain enzymes eliminate local fat deposits, cellulite, restore skin elasticity. This treatment is called enzymatic lipolysis or enzyme therapy.
- There are two generations of enzyme preparations:
the first generation is a triad consisting of lipase, hyaluronidase and collagenase. Each enzyme solves a specific problem. Lipase causes the breakdown of fat cells, reduces fat deposits in the volume. Hyaluronidase reduces puffiness in the intercellular space, which is important in the treatment of edematous cellulite. Collagenase stimulates the production of new collagen. This makes the skin supple.
the second contains lipase, lyase, collagenase and hyaluronic acid, which additionally moisturizes the skin.
Enzyme therapy is used for body contouring, when it is necessary to make body bends more feminine, smooth. Minimum required from 4 to 6 sessions with an interval of 7-14 days.
What areas for injections are most popular
Most often, lipolytic injections are used in such areas:
- underbelly,
- fat deposits on the hips,
- back under the shoulder blades,
- base of the neck (Dowager’s hump).
- lipomas on any area,
- lower thigh area, areas above the knees,
- breast glands (with gynaecomastia in men)
- waist modeling;
- patches above the knees;
- “ears” on the hips;
- underbelly;
- hands;
- buttocks, inner thighs.
Advantages and disadvantages of each method
The main advantages of lipolytics are:
- fairly quick effect;
- the ability to adjust individual zones;
- allow you to remove cellulite, reduce the layer of fat to 5 cm;
- minimum period of rehabilitation;
- quite persistent effect.
The disadvantages include:
- relative pain (even taking into account the introduction of an anesthetic);
- the possibility of scarring and bruising;
- allergic reactions;
- uneven effect (“troughs”) is possible;
- sagging and sagging skin in the area of weight loss.
Advantages of enzyme therapy:
- pronounced and lasting aesthetic result;
- lack of preservatives;
- hypoallergenicity;
- high level of security;
- the ability to mix individual cocktails for each patient;
- lipolysis occurs in combination with tissue lifting;
- the ability to adjust areas requiring “jewelry” accuracy;
- minimum discomfort during the procedure;
- lack of a rehabilitation period;
- minimal risk of complications.
The disadvantages include individual pain even when using an anesthetic.
When the result is visible
After the first session, the result will be visible. The maximum effect is manifested within two months after a course of procedures. For a more impressive result, we recommend combining lipolytic injections with our signature massages.
Is fat coming back?
Weight loss injections have an irreversible effect on adipocytes. Once destroyed, they do not reappear in the injection area.
Contraindications:
- pregnancy and breastfeeding
- blood clotting disorders
- infections at the injection sites
- kidney disorders
- diabetes mellitus
- medium and morbid stages of obesity